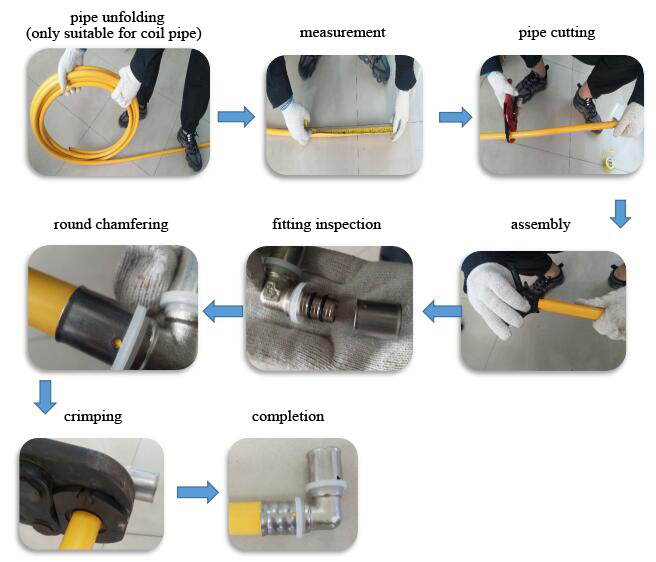
1.1 Preparation of materials and tools
Relevant materials and tools should be prepared according to the requirements of construction design, including pipes, fittings, shears, reamers, crimping tools and other materials required on the construction site.
1.2 Expansion and measurement
Expand the required multi-layer pipe (applicable for coiled pipe, not required for straight pipe), and measure the expanded multi-layer pipe according to the construction drawings or the actual requirements of the site.
1.3 Pipe cutting
Use pipe shears to cut the measured pipe.
1.4 Reaming
Use a reamer to round the cut multi-layer pipe, and chamfer the inside and outside of the pipe end.
1.5 fitting check
Before assembling pipes and fittings, check whether each fitting is complete (as shown in Figure 2).
1.6 Assembly
Insert the reamed pipe smoothly along the axial direction of the pipe and fitting, and check whether the pipe is in place through the observation hole on the stainless steel sleeve.
1.7 Crimping
Open the special crimping tool, select a crimping clamp block of appropriate specifications, one side of the crimping clamp block is close to the side of the plastic protective sleeve close to the stainless steel sleeve, and then crimp, after crimping in place, observe whether the two crimping clamp blocks are closed. (If not closed, adjust the crimp tool pressure until it can be crimped closed), release the crimp tool to complete the installation.
1.8 Connection Diagram

2.Construction and maintenance precautions
a. Multi-layer pipes, fittings and crimping tools must use our supporting products or other brand products approved by our company.
b. Multi-layer pipes and fittings should be stored indoors to avoid rain and direct sunlight.
c. Multi-layer pipes for gas shall be constructed in strict accordance with CECS 264-2009 "Technical Specifications for Construction Gas multi-layer Pipes - Pipeline Engineering".
d. During construction, should handle with care, do not bump each other, and do not rub against hard objects, to avoid any deformation and damage of pipes and fittings.
e.When expanding the pipe, the pipe should be placed on a soft surface or a flat hard surface, and the pressing force onto the pipe should be moderate to avoid damage to the pipe surface due to hard objects and deformation due to excessive pressing force.
f.When cutting the pipe, the cutting end should be perpendicular to the axis of the pipe, and there should be no obvious inclination, burrs, etc. (as shown in Figure 4)

g.The pipe must be reamed before installation to avoid difficulty in inserting, the sealing ring's out of position, and the sealing ring’s damaged (as shown in Figure 5).

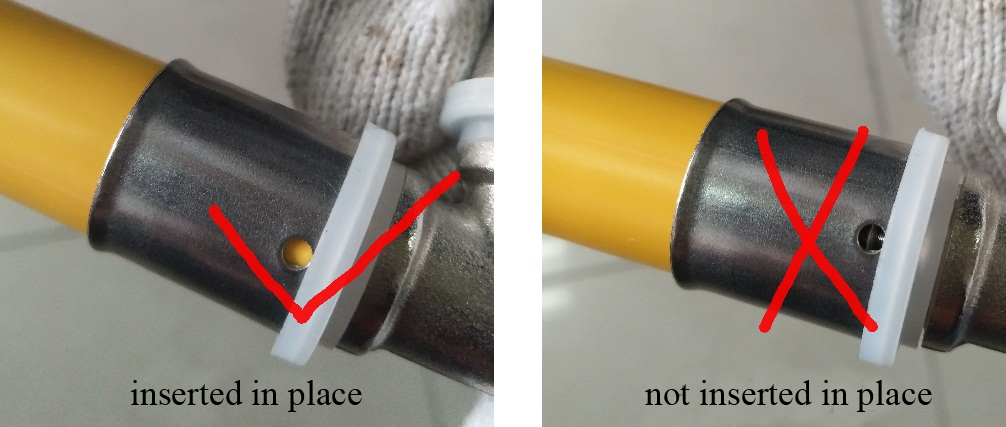
h. During assembly, the insertion of pipes and fittings must be uniformly applied in the axial direction and inserted smoothly to avoid displacement or damage of the seal due to excessive force (as shown in Figure 5). Observe whether the plug is in place (as shown in Figure 6).
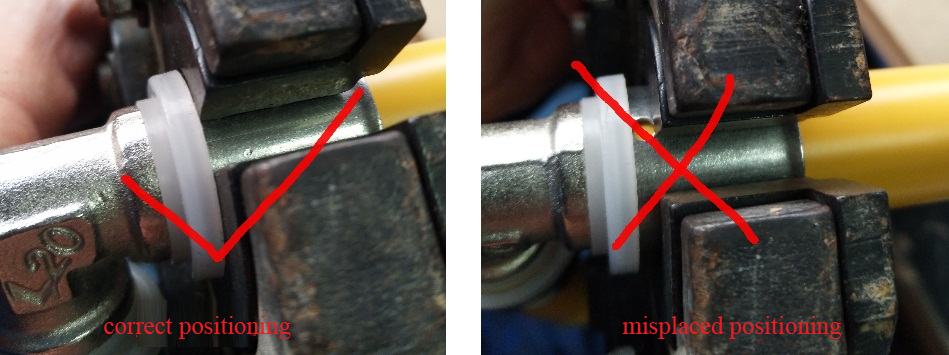
i. When crimping, the end face of the crimping pliers block must be close to the end face of the plastic socket (Figure 7). After the crimping is completed, observe whether the crimping pliers crimping module is completely closed (if it cannot be closed, the relevant mechanism of the crimping pliers can be adjusted Increase the pressure until it is closed. If the pressure is increased to the maximum and the pressure is still not closed, the crimping pliers can be declared scrapped. After adjusting or replacing the crimping tool, the crimping can be continued along the original indentation) (Figure 8), otherwise it may cause the pipe’s fall off. or leaks.
j.After the multi-layer pipes and fittings are scrapped, they should be handed over to a company with relevant qualifications for recycling.